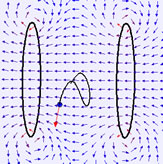

The EJS Helmholtz Coils Model shows a the magnetic field between two circular coils of wire. The default configuration, known as a Helmholtz coil, sets the separation distance D equal to the coil radius R. These values produce a nearly uniform magnetic field B between the coils
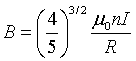
where I is the current, n is the number of loops in each coil, and μo is the magnetic permeability. The model includes the simulation of a charged particle trajectory in the vicinity of the coils.
Because Helmholtz coils are often used in experiments to produce nearly uniform magnetic fields, their use is discussed in many experimental physics laboratory manuals.
The analytic expression for the on-axis magnetic field is straightforward to derive and this derivation is often assigned for homework in physics textbooks.
A challenging theory problem is the derivation of the off-axis magnetic field in terms of elliptic integrals. This computer model computes the magnetic field using the Biot-Savart law and performing a numerical integration around each coil.
The Helmholtz Coils Model was created by Fu-Kwun Hwang at National Taiwan Normal University using the Easy Java Simulations (EJS) modeling tool. It was adapted to EJS version 4.1 by Robert Mohr and Wolfgang Christian at Davidson College. You can examine and modify a compiled EJS model if you run the model (double click on the model's jar file), right-click within a plot, and select "Open Ejs Model" from the pop-up menu. You must, of course, have EJS installed on your computer.
Information about Ejs is available at: <http://www.um.es/fem/Ejs/> and in the OSP ComPADRE collection <http://www.compadre.org/OSP/>.